AAAI 2023
Delving Deep into Pixel Alignment Feature for Accurate Multi-view Human Mesh Recovery
Kai Jia, Hongwen Zhang, Liang An, Yebin Liu
Tsinghua University
Abstract
Regression-based methods have shown high efficiency and effectiveness for multi-view human mesh recovery. The key components of a typical regressor lie in the feature extraction of input views and the fusion of multi-view features. In this paper, we present Pixel-aligned Feedback Fusion (PaFF) for accurate yet efficient human mesh recovery from multi-view images. PaFF is an iterative regression framework that performs feature extraction and fusion alternately. At each iteration, PaFF extracts pixel-aligned feedback features from each input view according to the reprojection of the current estimation and fuses them together with respect to each vertex of the downsampled mesh. In this way, our regressor can not only perceive the misalignment status of each view from the feedback features but also correct the mesh parameters more effectively based on the feature fusion on mesh vertices. Additionally, our regressor disentangles the global orientation and translation of the body mesh from the estimation of mesh parameters such that the camera parameters of input views can be better utilized in the regression process. The efficacy of our method is validated in the Human3.6M dataset via comprehensive ablation experiments, where PaFF achieves 33.02 MPJPE and brings significant improvements over the previous best solutions by more than 29%.
[arXiv] [Code]
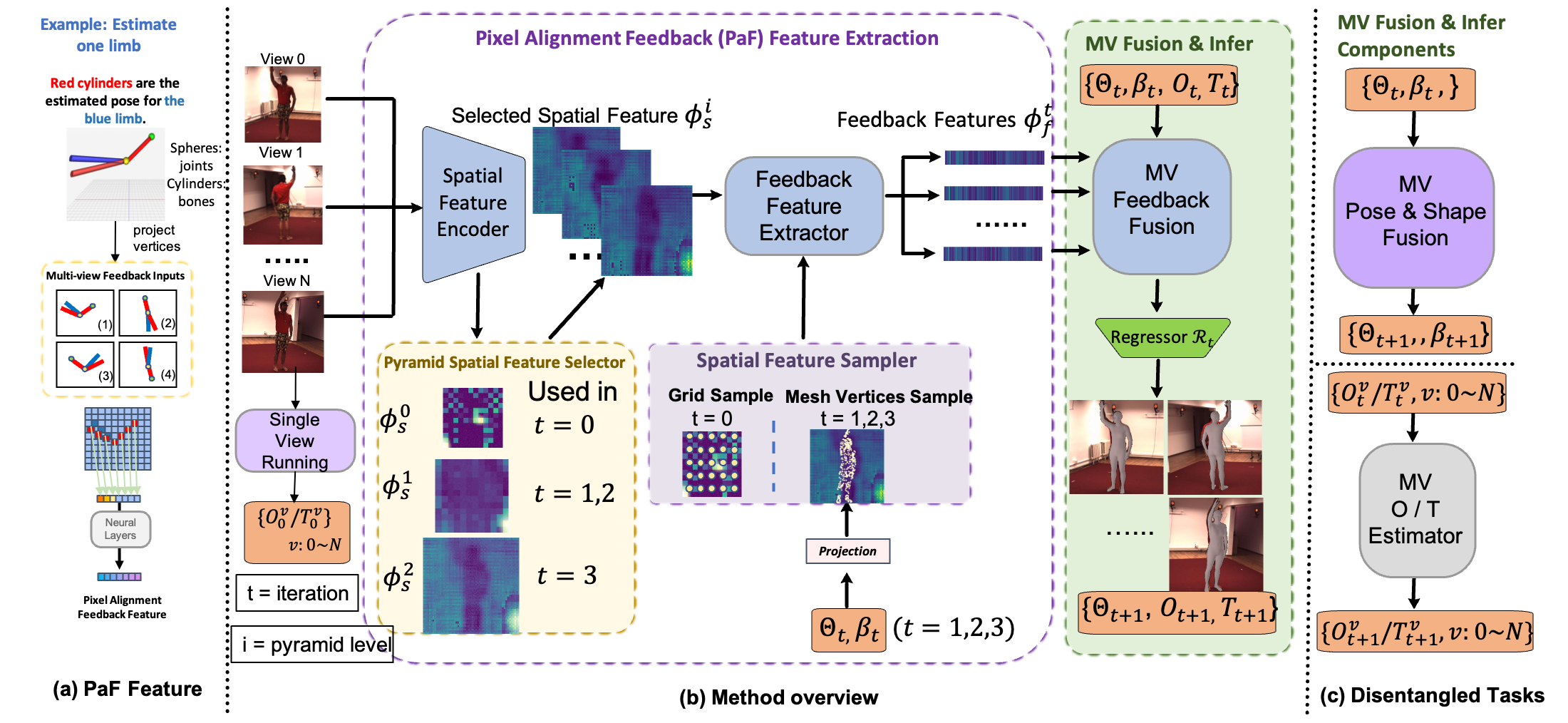
Fig 1. Overview of our proposed Pixel-aligned Feedback Fusion (PaFF) pipeline. (a) Pixel Alignment Feedback (PaF) Feature Extraction. (b) PaFF iteratively refines human body parameters’ estimation with the guidance of the PaF feature. (c) The task of multi-view feedback fusion is disentangled into three tasks - Multi-view Pose & Shape Fusion, Multi-view Orientation Estimation, and Multi-view Translation Estimation to incorporate camera parameters in the end-to-end model.
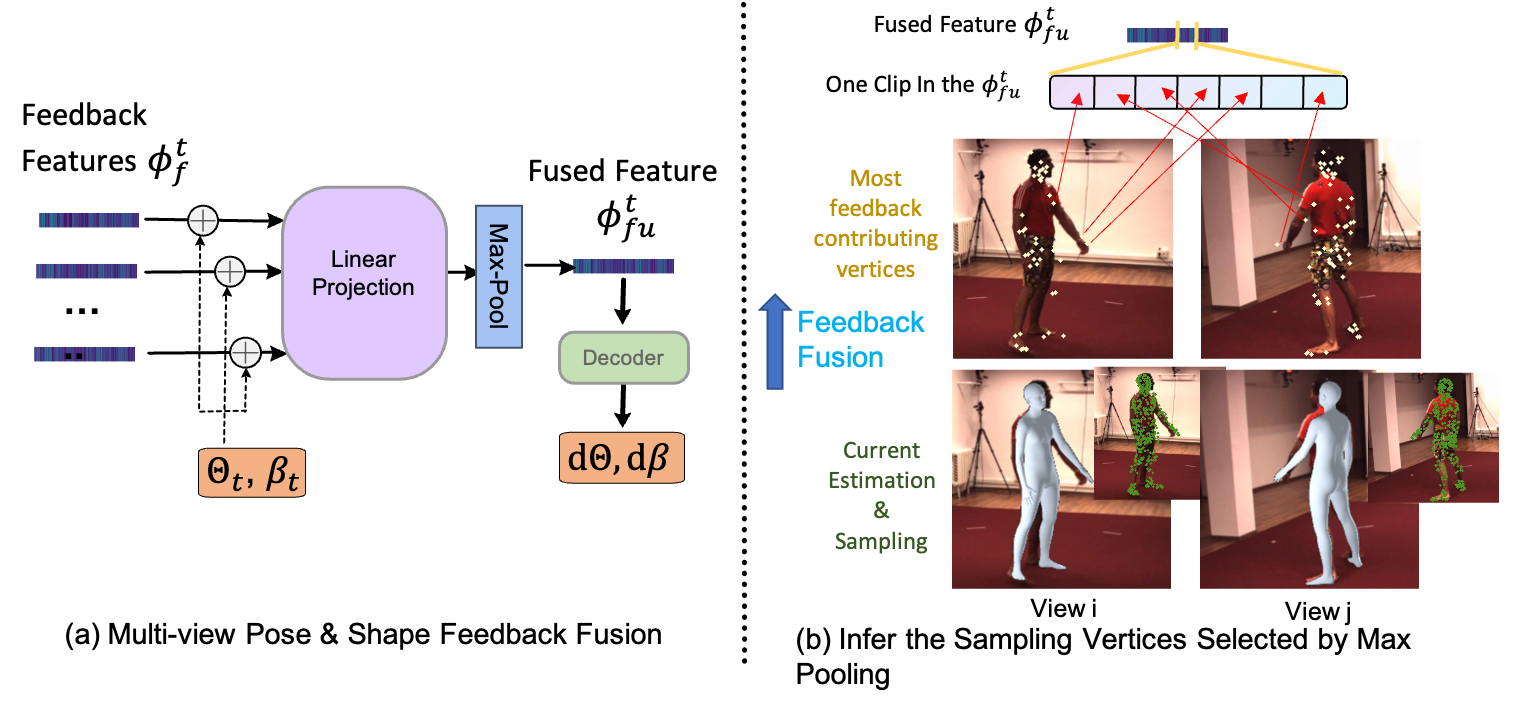
Fig 2. Multi-view Pose & Shape Feedback Fusion Module. a) The structure of pose & shape multi-view feedback fusion Module. b) Visualize vertices selected by max-pooling: The estimated meshes from the previous iteration and the sampled vertices are shown at the bottom. In the top images, we visualize the sampling vertex in each view that contributes most to one feature dimension of the fused feature. By looking at the selected vertices on the left arm and legs, we can find that the vertices which reflect more estimation misalignment are easier to be chosen.
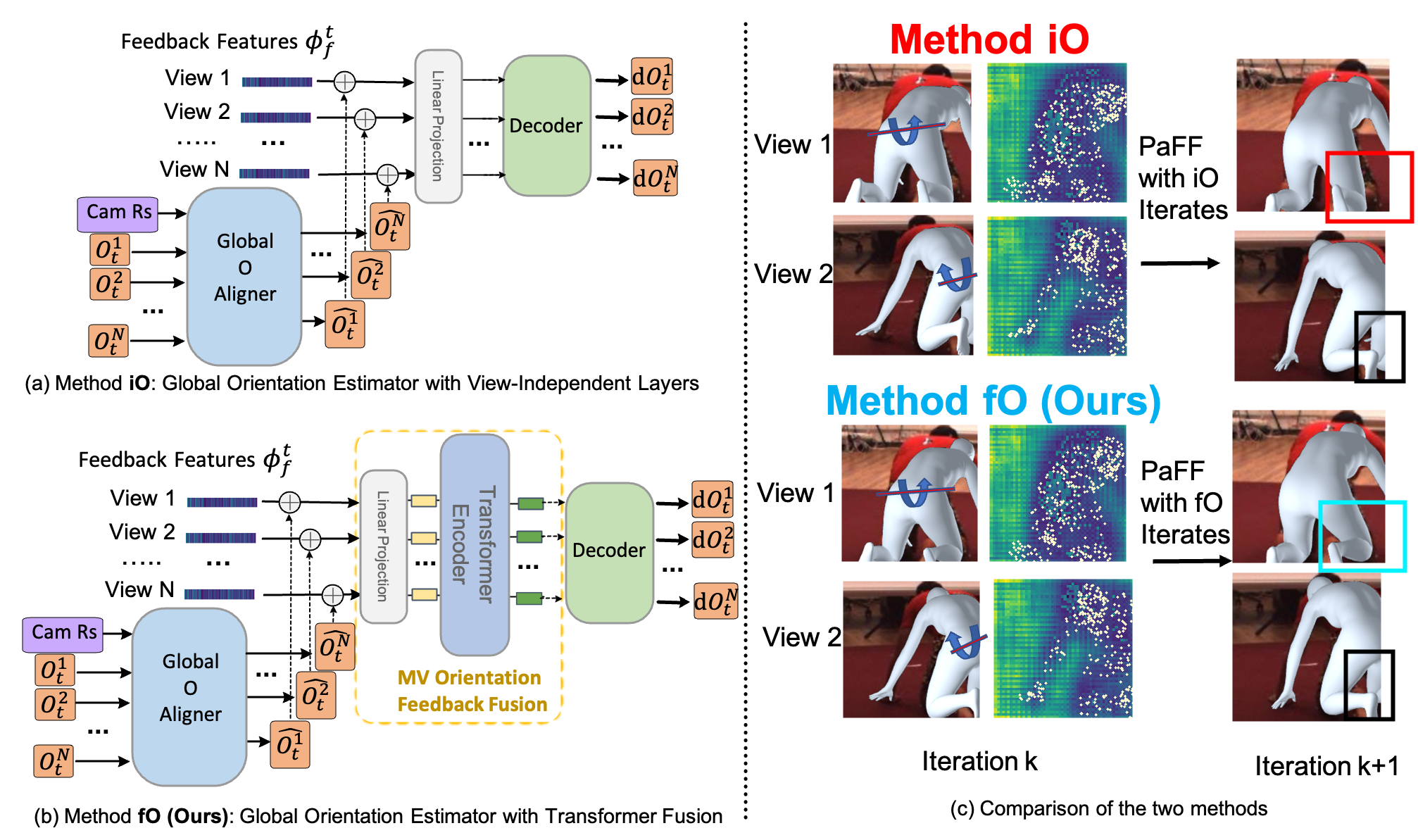
Fig 3. Global Orientation Estimator. (a) Method iO and (b) Method fO are two options for Global Orientation Estimator; (c) shows the motivation of method fO that uses transformer fusion to collect multi-view body parts mis-alignment signals in order to avoid depth ambiguity and occlusion problems. Estimated models and feature sampling are visualized in the left images, while updated estimations are shown in the right images. Blue arrows indicate the correction rotation needed for each view’s estimation. Comparing the refinement effect in one iteration (k=2) of the two methods, method fO performs better in orientation estimation, which also leads to a better estimation of the right leg.
Results
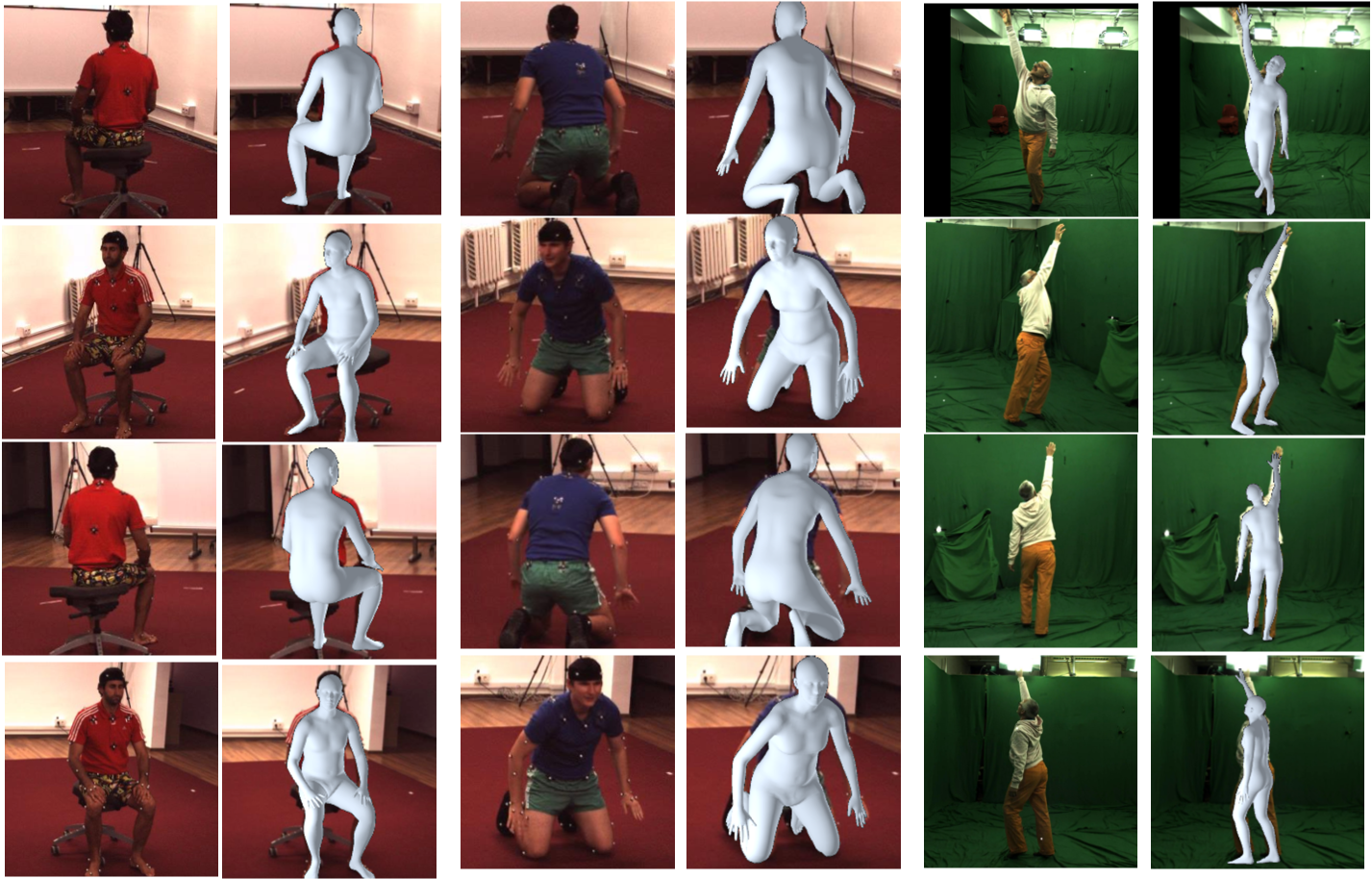

Fig 4. Qualitative results on Human3.6M and MPI-INF-3DHP. Each row means a different view.
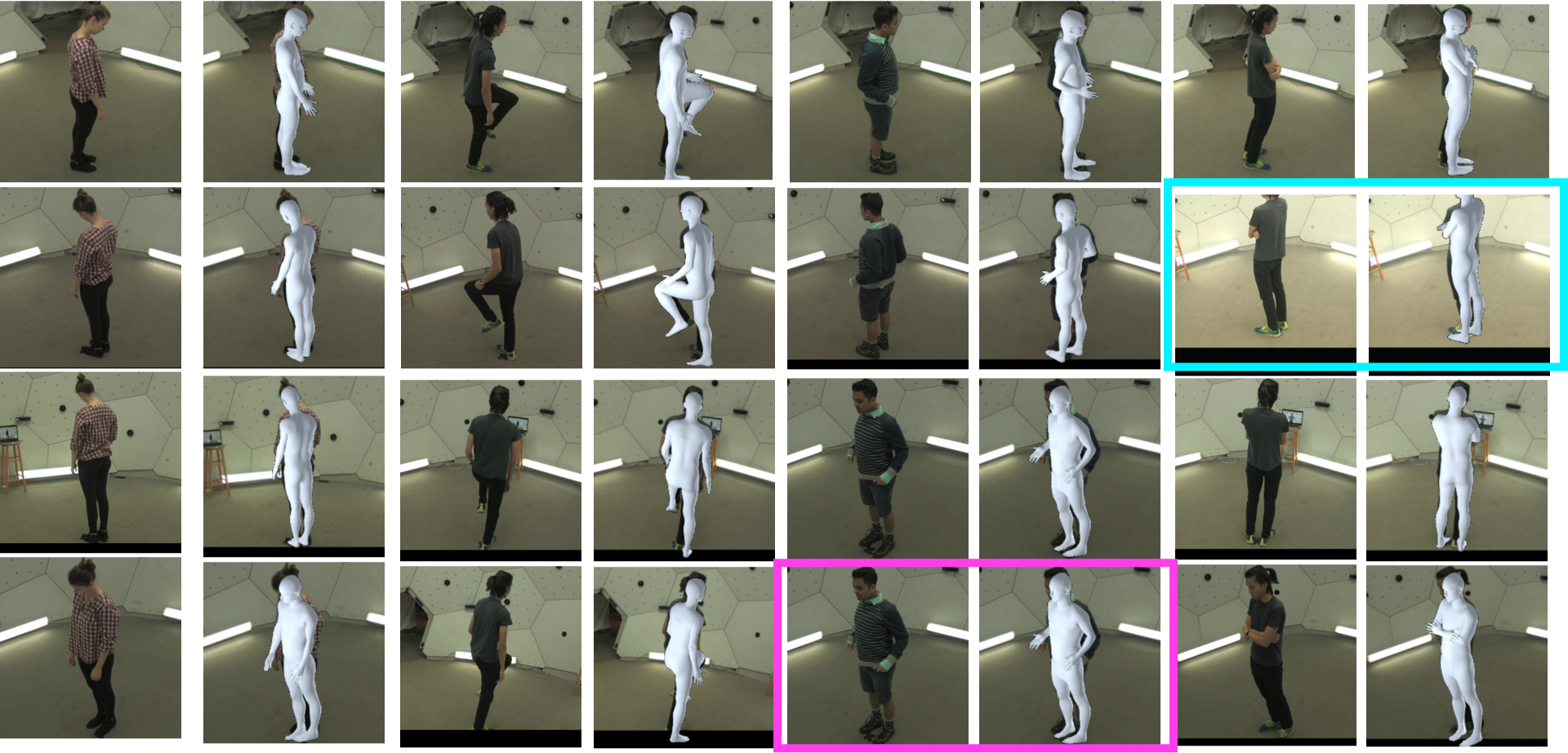

Fig 5. Predictions of Our PaFF Estimations on MTC (Xiang, Joo, and Sheikh 2019), which shows the generalization ability for our method. The results are from a test set of MTC after a mix-training on Human3.6M and MTC. The third example shows feeding one repetitive image (inside the pink box). The fourth example shows changing one viewpoint (inside the blue box). Both of the results show the robustness of our PaFF in viewpoint changing. More examples can be seen in the video demo.
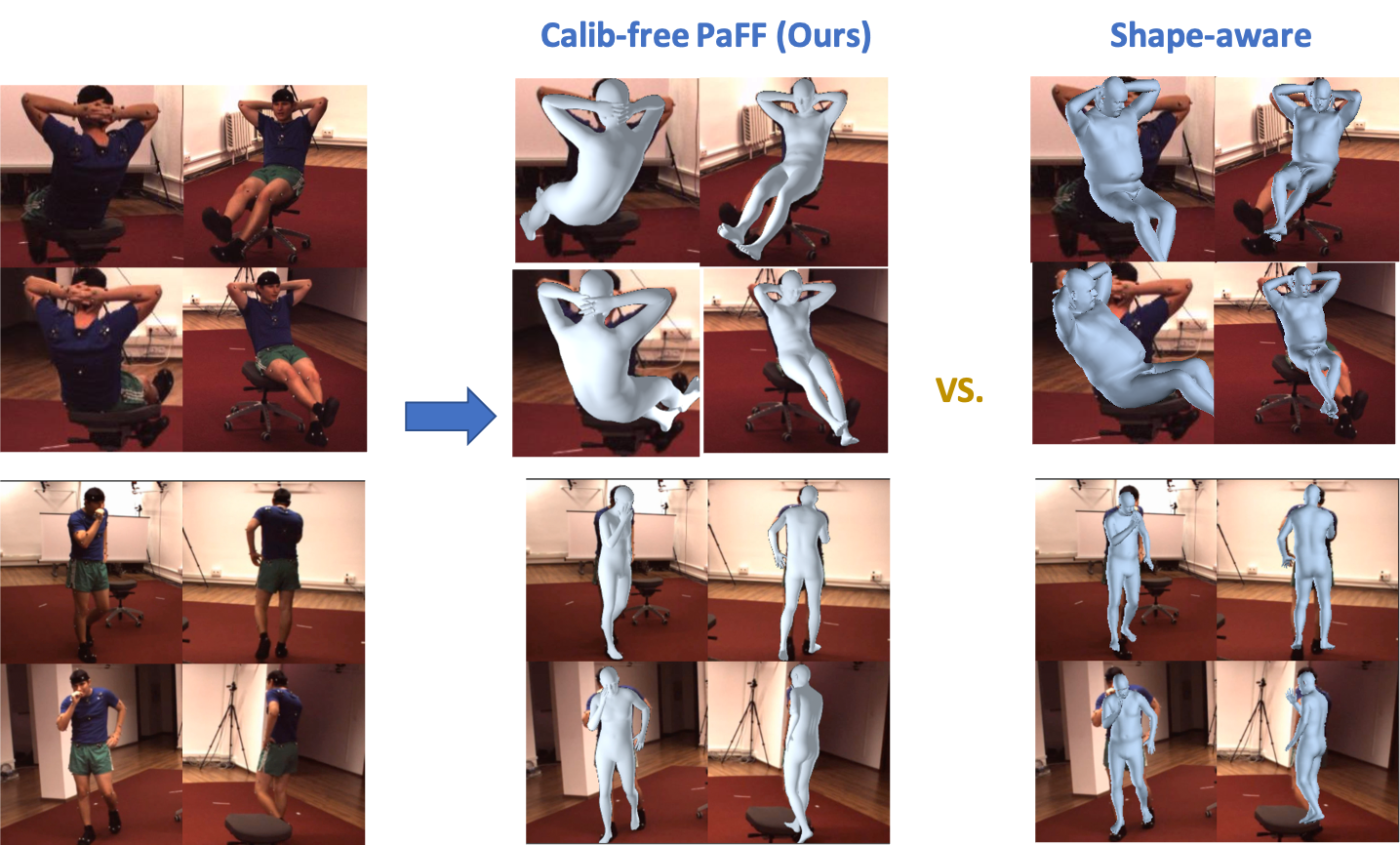
Fig 6. Visualization of the effect of Multi-view PaF Feature by comparing the calibration-free PaFF and Shape-aware (Liang and Lin 2019) in two cases.
Technical Paper
Presentation
Video Demo [Human3.6M]
Video Demo [MTC]
Comparison Video
Supplementary Material
Citation
Kai Jia, Hongwen Zhang, Liang An, Yebin Liu. "Delving Deep into Pixel Alignment Feature for Accurate Multi-view Human Mesh Recovery". AAAI 2023
@InProceedings{jia2023paff,
title={Delving Deep into Pixel Alignment Feature for Accurate Multi-view Human Mesh Recovery},
author={Jia, Kai and Zhang, Hongwen and An, Liang and Liu, Yebin},
booktitle={Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence},
month={Febuary},
year={2023},
}